
The puzzling surge in Arctic Warming has long eluded a comprehensive explanation. However, recent research from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology offers a groundbreaking proposition: could major earthquakes be the unexpected trigger behind the rapid Arctic warming?
1. Climate Anomaly Beyond Human Activity
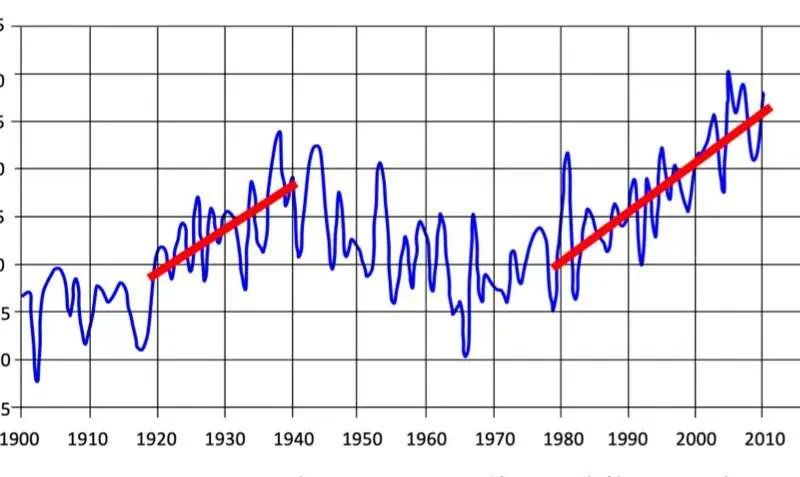
Amidst the prevailing narrative attributing global warming solely to human-induced greenhouse gas emissions, abrupt temperature escalations have remained an enigma. Particularly in the Arctic, the rise in temperatures witnessed in the 1920s, and 30s, and the persistent warming trend since the 1980s defy conventional explanations.
2. The Drivers of Arctic Climate Shifts
Scientist Leopold Lobkovsky, a distinguished member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, advocates an unconventional theory in the realm of climate science. His research posits that geodynamic forces, specifically major earthquakes in the Aleutian Arc region, might be the catalysts behind these erratic temperature fluctuations.
3. Unraveling the Connection: Earthquakes and Temperature Surge
Lobkovsky’s inquiry revolves around three pivotal queries. Firstly, he probes the correlation between major earthquake occurrences and sudden temperature spikes of Arctic Warming. Historical analysis suggests a striking alignment, indicating a temperature surge of 15 to 20 degrees preceding seismic events.
4. Tracing the Path: Understanding Propagation Mechanisms
Addressing the propagation mechanism becomes the second focal point. Lobkovsky’s team deploys a dynamic model illustrating the transmission of tectonic waves, estimating their propagation rate at approximately 100 kilometers per year. This accounts for the delay between seismic occurrences and subsequent temperature surges, requiring 15 to 20 years to traverse the 2000-kilometer distance.
5. The Methane Enigma Unveiled
Finally, the research dives into the impact of methane emissions. Disturbances from seismic waves in the Arctic Warming shelf region exert minute stresses on the lithosphere, disrupting gas hydrates and permafrost. This disturbance leads to the release of methane into the atmosphere, exacerbating the greenhouse effect and consequently contributing to regional warming.
6. Lobkovsky’s Insights and Implications
Academician Lobkovsky concludes, emphasizing the cohesive link between major earthquakes and Arctic warming. He stresses the pivotal role of stress transfer within the lithosphere, its disruptive impact on gas hydrates and permafrost, and the resulting methane release. This comprehensive scenario fills the gaps left by previous models, elucidating the abrupt temperature surges in the Arctic.
The unveiling of this seismic-earthquake connection to Arctic warming presents a paradigm shift in climate science, challenging conventional perceptions and urging further exploration into the interplay between geodynamic forces and climatic phenomena.
Related:
[…] Unveiling a New Perspective: Earthquakes and Arctic Warming […]